we embark on a fascinating journey through the realm of electromagnetism and delve into the profound contributions of James Clerk Maxwell. Maxwell's groundbreaking equations revolutionized our understanding of electricity, magnetism, and their intricate relationship.
We unravel the fundamental principles encapsulated within Maxwell's equations, which elegantly describe how electric and magnetic fields interact and propagate through space. These equations not only unified the fields of electricity and magnetism but also predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves, laying the groundwork for the development of modern technologies such as radio, television, and wireless communication.
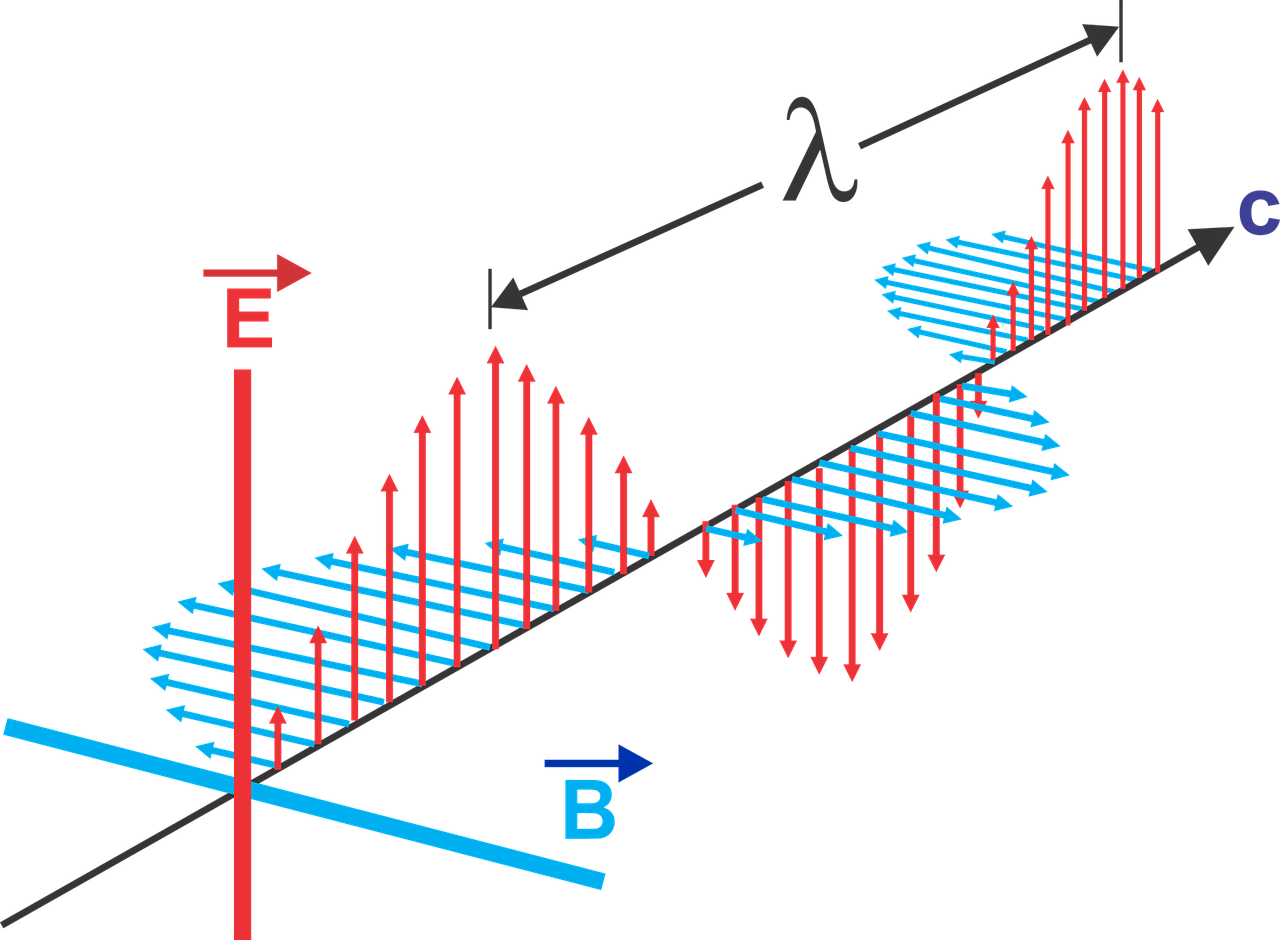
1. Development of the Theory:
Michael Faraday (early 1800s):
- Discovered electromagnetic induction, which is the process by which a changing magnetic field can produce an electric current.
- His work led to the development of electric generators and transformers.
James Clerk Maxwell (mid-1800s):
- Unified the laws of electricity and magnetism into a set of four equations, now known as Maxwell's equations.
- Maxwell's equations predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves, which were later discovered by Heinrich Hertz.
2. Key Tenets of Electromagnetism:
- Electric and magnetic fields are related to each other.
- A changing electric field can produce a magnetic field.
- A changing magnetic field can produce an electric field.
- Electromagnetic waves can propagate through space.
- The speed of light is the same as the speed of electromagnetic waves.
3. Experimental Verification:
- Faraday's experiments on electromagnetic induction: He showed that a changing magnetic field can produce an electric current.
- Hertz's experiments on electromagnetic waves: He showed that electromagnetic waves can propagate through space.
Many other experiments: Over the years, many other experiments have been conducted to verify the predictions of Maxwell's equations.
4. Technological Applications:
- Electricity: The generation, transmission, and use of electricity is based on the principles of electromagnetism.
- Radio and television: Radio and television waves are electromagnetic waves.
- Radar: Radar uses electromagnetic waves to detect objects.
- Mobile phones: Mobile phones use electromagnetic waves to communicate with each other.
- Wireless networks: Wireless networks use electromagnetic waves to transmit data.
5. Sociocultural Impact:
- Electromagnetism has revolutionized the way we live and work.
- It has made possible the development of many new technologies that have had a profound impact on society.
- It has also raised ethical questions about the use of electromagnetic waves, such as the potential for health problems from exposure to radio waves.
Electromagnetism is a fundamental theory of physics that has had a profound impact on our understanding of the universe.
'Science' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 생명의 퍼즐을 푼다: 진화, 환경생물학, 생물 다양성 (0) | 2024.06.06 |
|---|---|
| Unveiling the Doppler Effect; Exploring Christian Doppler's Phenomenon (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| Genetics (Gregor Mendel): Exploring the Contributions of Gregor Mendel (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| Evolution Unraveled: Exploring Charles Darwin's Theory (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| Theory of Gravity; Exploring the Theories of Isaac Newton and Albert Einstein (0) | 2024.06.06 |



